Übersicht Handschuhzertifizierungen
The European standard DIN EN420 defines the general requirements, test methods and marking of safety gloves. Among other things, this certification ensures that the materials used, and their processing, do not adversely affect the health of the person wearing them.
In addition, safety gloves covered by DIN EN420 are tested for the following properties:
- Ergonomics and comfort
- Material composition and labelling
- Resistance of the glove material to water penetration
- Lightness and stability of the glove material
If a glove fulfils the requirements of this standard, it is marked using the EN420 logo.

For a glove to be certified in accordance with DIN EN388:2016, it must first be successfully tested for the general requirements of DIN EN420.
First, we would like to inform you that all safety gloves are merely resistant to cuts and punctures! Safety gloves offer NO absolute protection against cuts or punctures!
The European standard DIN EN388:2016 defines the requirements, the individual test methods and the marking of safety gloves against mechanical risks. This certification tests the glove for abrasion resistance, cut resistance, tear resistance and puncture resistance.
The values obtained are classified in categories and can be read using the pictogram (sign with hammer).
The following principle applies here: The higher the category, the better the protection!

You can find this sign on our gloves in the following places:
- on the glove packaging
- in the booklet, which is enclosed in the packaging
- on a small label inside the glove
Test methods and evaluations of DIN 388:2016 at a glance
For a more detailed explanation of the individual evaluations and test methods, please refer to the values of our glove COP CR214TS in the example below.

Abrasion resistance: Category 2
Test method:
A rotating disc with sandpaper scrubs the glove material.
It is determined how many cycles are needed until the material wears through.
Category 0: 0 to 99 cycles
Category 1: 100 to 499 cycles
Category 2: 500 to 1999 cycles
Category 3: 2000 to 7999 cycles
Category 4: 8000 cycles or more
Cut resistance (COUP test): Category 3
Test method:
A rotating circular knife cuts across the glove material from left to right at constant speed and force (5 newtons). For simplicity, the result is given with an index value. This value comprises the number of cycles that are needed to cut through the material, and the degree of wear of the used blade.
Category 0: < Index 1,2
Category 1: ≥ Index 1,2
Category 2: ≥ Index 2,5
Category 3: ≥ Index 5
Category 4: ≥ Index 10
Category 5: ≥ Index 20
*Categorie X
*If the result of this test method is marked with an "X", the glove material has EXCEEDED the requirements of this test!
The glove material was not cut during the test and the used blade became blunt.
However, to still obtain a value for cut resistance, another test method for cut resistance was introduced in the context of the new DIN EN388:2016. This is the TDM test (pursuant to ISO 13997). You can find further information about the TDM test below.
Tear resistance: Category 3
Test method:
The glove is fixed in a traction machine.
It is determined what force is needed for the glove to tear.
Category 0: 0 to 9.9 newtons
Category 1: 10 to 24.9 newtons
Category 2: 25 to 49.9 newtons
Category 3: 50 to 74.9 newtons
Category 4: 75 newtons or more
Puncture resistance: Category 4
Test method:
A test nail is used to determine which force is needed to puncture the glove material.
Category 0: 0 to 20 newtons
Category 1: 20 to 59.9 newtons
Category 2: 60 to 99.9 newtons
Category 3: 100 to 149.9 newtons
Category 4: 150 newtons or more
Please note that this test provides no indication of protection against injection needles or cannulae! In our view, needles, injection needles and cannulae are classified as hazardous!
Cut resistance (TDM test): Category C
As part of the EN388:2016, another cut resistance test (also called the TDM test) for safety gloves was introduced in accordance with EN ISO 13997.
The result of this test gives an indication of the cut resistance if the category of the first cut resistance test (COUP test) is marked with an "X".
Test method:
A straight blade cuts across the glove material from left to right with varying degrees of force. After each cut, the blade is renewed, and the degree of force is increased.
It is determined what force is needed to cut through the material.
Category A: 2 newtons
Category B: 5 newtons
Category C: 10 newtons
Category D: 15 newtons
Category E: 22 newtons
Category F: 30 newtons
Please note that both tests for cut resistance (COUP and TDM test) are two completely different test methods. Both results are not comparable with each other.
The European standard DIN EN 13594 defines the requirements and test methods for safety gloves for motorcyclists.
During the test, the glove model, and the material that is processed for it, is tested for protection against impacts from falls and collisions.
If a glove meets the requirements of this standard, an additional marking in the pictogram with a "P".
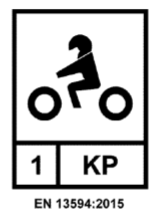
You can find this sign on our gloves in the following places:
- on the glove packaging
- in the booklet, which is enclosed in the packaging
- on a small label inside the glove
The European standard DIN EN 407 defines the requirements and test methods for safety gloves against thermal risks (heat and/or fire).
Please note that DIN EN 407 is not applicable to applications such as fire fighting or working with welding equipment!
A glove can only be tested for the requirements of DIN EN 407 if it has achieved at least category 1 in the areas of abrasion and tear resistance within the scope of the test procedure of DIN EN388:2016!
During the test, the glove model is tested for six properties.
The values obtained are classified in categories and can be read using the pictogram (sign with flame).
The following principle applies here: The higher the category, the better the protection!
- burning behaviour (categories 0 - 4)
- contact heat (categories 0 – 4)
- convective heat (categories 0 – 4)
- radiant heat (categories 0 – 4)
- small splashes of molten metal (iron only) (categories 0 - 4)
- large quantities of molten metal (iron only) (categories 0 - 4)
A glove can also fail individual tests. Such cases are marked with the letter "X".

ASTM F 2878-10 or ASTM F 2878-19






















